In today’s world, passwords and PINs are no longer enough to keep our digital lives safe. With cyberattacks becoming more advanced, companies and governments are looking for stronger ways to protect data and identities. This is where biometrics comes in.
Biometrics uses unique human features like fingerprints, face, iris, or voice to identify a person. Unlike passwords, you cannot forget or easily steal these traits. But setting up biometric systems on-site is often expensive and complicated.
To solve this problem, a new model has emerged — Biometrics-as-a-Service (BaaS). Instead of building everything from scratch, businesses can now use cloud-based biometric services on demand. This makes biometric security more accessible, cost-effective, and easier to scale.
In this blog, we’ll explain what Biometrics-as-a-Service is, how it works, its benefits, challenges, use cases, top providers, and the future of this fast-growing technology.
What Is Biometrics-as-a-Service?
Biometrics-as-a-Service (BaaS) is a cloud-based solution that delivers biometric recognition and authentication through the internet.
Instead of companies buying expensive biometric hardware and software, they can subscribe to BaaS platforms and use biometrics through simple integrations like APIs or SDKs.
For example:
- A mobile app can use a cloud-based face recognition service to verify users.
- A bank can use fingerprint or iris authentication through a BaaS provider to secure transactions.
This is different from traditional biometric systems, where all the data storage, processing, and software must be managed in-house. With BaaS, everything happens in the cloud, making it much faster and cheaper to deploy.
How Does Biometrics-as-a-Service Work?
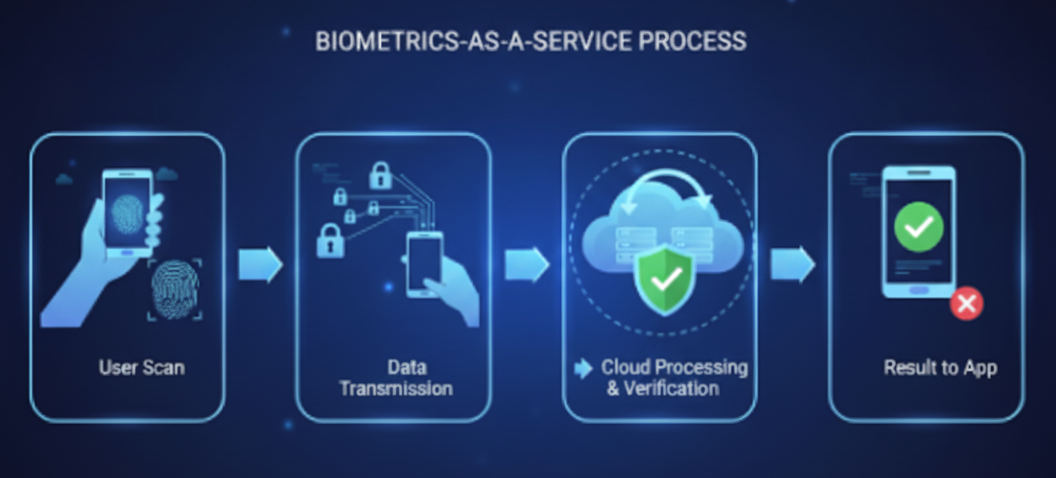
Biometrics-as-a-Service may sound complex, but the workflow is quite straightforward. Here’s how it usually works:
- Data Collection
-
-
- A device or app collects biometric data (fingerprint, facial scan, voice sample, or iris scan).
-
- Secure Transmission
-
-
- The collected data is securely sent to the cloud server of the BaaS provider using encryption.
-
- Processing & Matching
-
-
- In the cloud, the biometric data is compared against stored templates or databases to verify or identify the person.
-
- Response Back
-
-
- The result (success or failure) is sent back to the application in real-time.
-
- Integration via APIs/SDKs
-
- Developers integrate BaaS into their apps using APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) or SDKs (Software Development Kits).
This process ensures security, speed, and ease of use without requiring local infrastructure.
Key Features of Biometrics-as-a-Service
Here are some of the most important features of BaaS:
- Cloud Scalability: Services can expand easily as user demand grows.
- Multi-Modal Support: Includes fingerprints, face recognition, iris scans, voice recognition, and even behavioral biometrics (like typing patterns).
- On-Demand Access: Companies can use biometric services only when they need them.
- Easy Integration: APIs and SDKs allow businesses to quickly add biometrics into apps and platforms.
- Flexible Pricing: Subscription or pay-as-you-go models make it cost-effective.
- Security Enhancements: Providers often use AI and machine learning for fraud detection and accuracy improvements.
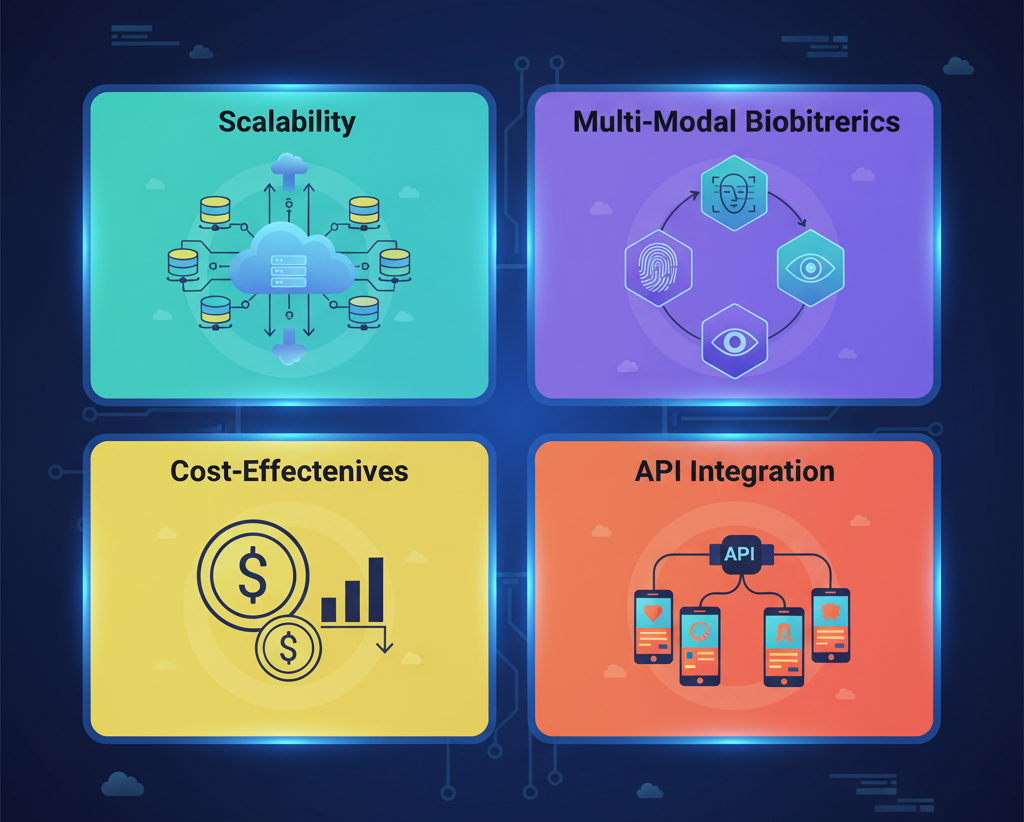
Advantages of Biometrics-as-a-Service
BaaS comes with several strong benefits:
1. Scalability
No matter how many users you have, cloud-based systems can handle growth smoothly without additional infrastructure.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Businesses avoid the huge upfront costs of buying biometric hardware and servers. Instead, they pay for what they use.
3. Faster Deployment
With ready APIs, companies can integrate biometrics into apps in weeks instead of months or years.
4. Accessibility
Even small and medium-sized businesses can now adopt biometrics, which was earlier limited to big corporations.
5. Enhanced Security
Centralized cloud platforms often include advanced monitoring, encryption, and regular updates to fight fraud.
6. Flexibility
Companies can choose different biometric methods based on their needs — fingerprint for employees, facial recognition for customers, or voice for call centers.
Challenges and Concerns with BaaS
Like any technology, BaaS also comes with challenges:
1. Data Privacy
Storing sensitive biometric data in the cloud raises concerns about misuse and hacking. Regulations like GDPR (Europe) and HIPAA (US healthcare) must be followed.
2. Dependence on Internet
Since BaaS runs in the cloud, downtime or poor connectivity can cause authentication delays.
3. Vendor Lock-In
Once a company integrates with a specific provider, switching to another service may be difficult.
4. User Trust Issues
Many users are still uncomfortable with their biometric data being stored by third parties.
5. Compliance Challenges
Different industries have strict laws regarding how biometric data should be stored, used, and shared.
Use Cases of Biometrics-as-a-Service
BaaS is already being used in many industries. Here are the most common applications:
1. Banking & Financial Services
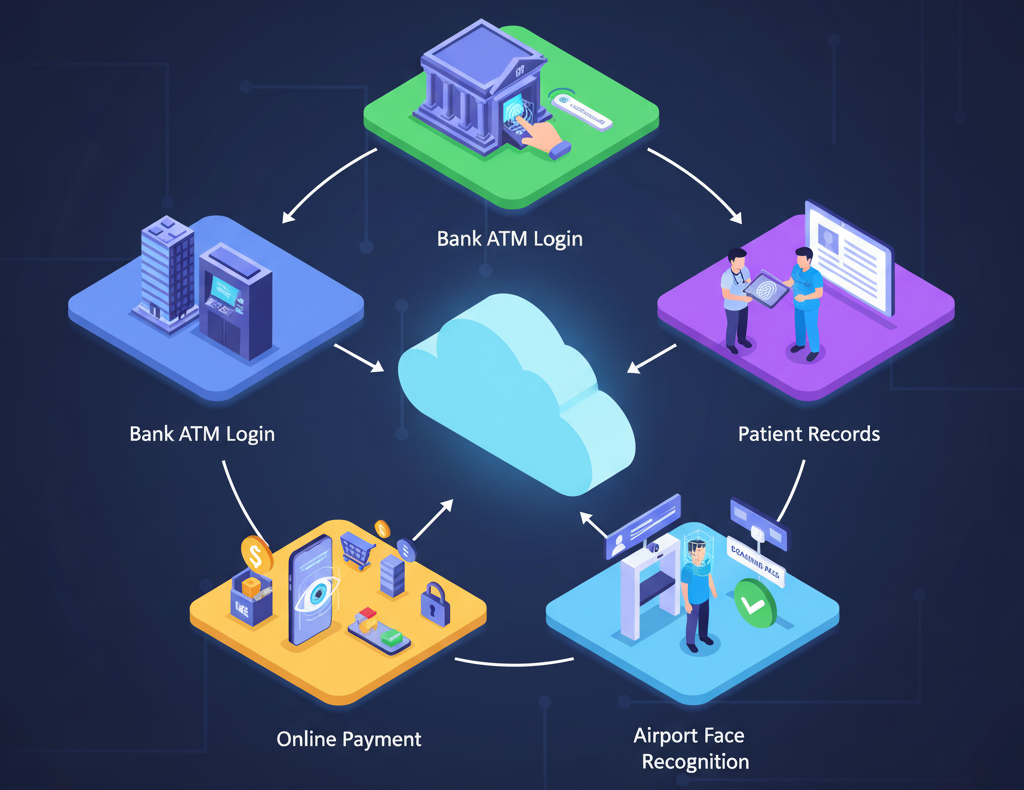
- Biometric authentication for secure mobile banking.
- Preventing fraud in online transactions.
- Customer verification during account opening.
2. Healthcare
- Patient identification and access control.
- Secure access to medical records.
- Remote telehealth verification.
3. Government & Public Sector
- National digital IDs and passports.
- Border control and immigration.
- Voter registration and e-governance platforms.
4. Retail & E-commerce
- Password-free logins for shoppers.
- Biometric payments at checkout.
- Personalized customer experiences.
5. Enterprise Security
- Employee attendance and access control.
- Remote work authentication.
- Protecting sensitive company systems.
Biometrics-as-a-Service vs Traditional Biometric Systems
Here’s how BaaS compares with traditional models:
| Feature | Traditional Biometrics | Biometrics-as-a-Service |
| Deployment | Slow, complex | Fast and easy via APIs |
| Cost | High upfront investment | Pay-as-you-go, affordable |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable |
| Maintenance | Managed in-house | Managed by provider |
| Flexibility | Rigid systems | Multi-modal, customizable |
Leading Providers of Biometrics-as-a-Service
Some of the top companies offering BaaS solutions include:
- Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services – Offers facial and speech recognition APIs.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Provides biometric identity and fraud detection solutions.
- BioID – Specializes in face recognition and liveness detection.
- NEC Corporation – Known for large-scale biometric cloud deployments.
- Aware Inc. – Provides fingerprint, face, and voice biometrics as cloud services.
Future of Biometrics-as-a-Service
The future of BaaS looks very promising:
- AI & Machine Learning will make biometric recognition faster and more accurate.
- Multi-Modal Biometrics (using multiple traits together) will reduce fraud even further.
- Integration with IoT devices like smart homes, cars, and wearables will grow.
- Global Adoption will increase in banking, healthcare, government, and consumer apps.
- Regulatory Frameworks will evolve to ensure security and trust.
Conclusion
Biometrics-as-a-Service is transforming the way we secure identities in a digital-first world. By combining the power of biometrics with the scalability of the cloud, BaaS offers businesses a reliable, cost-effective, and future-ready solution.
While there are challenges around privacy, trust, and compliance, the benefits far outweigh the risks. From banking to healthcare, government to retail, industries across the globe are already embracing this model.
In the coming years, Biometrics-as-a-Service will likely become the standard for identity verification and security, helping organizations stay ahead in the fight against cybercrime while offering users a safer, faster, and more convenient digital experience.




