The internet has become an essential part of our daily lives — from social media and gaming to e-commerce and streaming. But as more children and teenagers go online, concerns about digital safety are increasing worldwide. Governments, parents, and companies are now under growing pressure to make the internet a safer place for minors.
This is where age verification comes in.
In simple terms, age verification is the process of confirming that a user meets a platform’s minimum age requirement. It helps ensure that people accessing certain online content, products, or services are legally and safely allowed to do so.
In 2025, age verification has become a key part of online compliance, trust, and user protection. This blog will help you understand what age verification is, why it matters, the methods used, challenges faced, and what the future holds for this growing field.
Understanding Age Verification: Core Concepts
What Is Age Verification?
Age verification is a process used by websites, apps, and businesses to confirm a user’s real age before granting access to restricted content or services.
For example:
- An e-commerce site must verify that a buyer is over 18 before selling alcohol or tobacco.
- A gaming platform must confirm that players meet legal age limits.
- Social media sites may verify that users are above 13, following international child protection rules.
There are three related terms that are often used together but have different meanings:
- Age Verification: Confirms a user’s age with official documents (like a passport or ID).
- Age Estimation: Uses technology (like facial recognition or AI) to guess a person’s age.
- Age Assurance: A broader term that includes both verification and estimation methods to ensure age-appropriate experiences.
The key stakeholders involved in the process are:
- Platforms and Businesses: Responsible for compliance and user safety.
- Users: Who provide information or consent.
- Regulators: Who set and enforce the rules.
- Parents and Guardians: Who rely on verification systems for child protection.
Age Verification vs. Age Estimation
| Feature | Age Verification | Age Estimation |
| Definition | Confirms exact age using documents like a passport or ID card. | Predicts approximate age using AI or biometrics. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy and legal validity. | Moderate accuracy; relies on algorithms. |
| User Experience | Can add friction due to document upload. | Seamless and fast for users. |
| Best Use Cases | Legal compliance in adult, gaming, or financial sectors. | Quick checks for age-appropriate content or ads. |
In short: Verification is confirmatory and used where the law requires proof. Estimation is predictive and used for smoother user experiences.
The Age Verification Ecosystem
The ecosystem includes multiple players working together to ensure compliance and security:
- Platforms and websites that need to verify users.
- Third-party verification providers offering ID scanning, AI tools, or databases.
- Regulatory bodies that define compliance standards and penalties.
How it works (simplified):
- A user tries to access restricted content.
- The system requests age confirmation.
- Verification is done through ID upload, face scan, or data check.
- The system approves or denies access based on verified age.
Why Age Verification Matters Today
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
In 2025, governments around the world are tightening age verification requirements.
Here are some major regulations:
- European Union:
-
-
- The Digital Services Act (DSA) and GDPR require strong user verification to protect minors.
-
- United Kingdom:
-
-
- The Online Safety Act enforces strict content moderation and age verification for adult and social platforms.
-
- United States:
-
-
- Over 19 states have passed or proposed laws demanding age checks for certain online services.
-
- Australia:
-
- Draft laws are being reviewed for national age verification standards.
Non-compliance can lead to:
- Heavy fines and penalties
- Legal action and brand damage
- Platform restrictions or removal from app stores
Certain industries — like gaming, e-commerce, social media, and adult entertainment — are under special scrutiny for compliance.
Child Protection and Safety
One of the main goals of age verification is protecting minors online.
- It prevents underage access to gambling, alcohol, and explicit content.
- It helps parents control digital exposure for their children.
- It supports mental health and emotional development by shielding kids from harmful or mature materials.
In short, age verification helps create a safer digital environment that supports both freedom and responsibility.
Business and Brand Protection
Businesses also benefit from implementing age verification:
- Fraud prevention: Reduces identity theft and fake account creation.
- Brand reputation: Shows responsibility and compliance.
- Operational safety: Avoids regulatory penalties.
- Competitive advantage: Builds customer trust and market credibility.
In today’s privacy-aware environment, brands that prioritize safety gain more loyalty and respect.
Consumer Trust and Experience
Age verification, when done right, helps build consumer confidence.
Users feel safer knowing a platform protects privacy and prevents misuse. It also shows the brand cares about responsibility and transparency.
When verification systems are fast and frictionless, they can even enhance the user experience rather than disrupt it.
Age Verification Methods: Comprehensive Analysis
1. Document-Based Verification

This is the most traditional and legally accepted method.
How it works:
- Users upload a government-issued document like a passport or driver’s license.
- The system checks its authenticity using OCR (optical character recognition) and AI tools.
Pros:
- Highly accurate and compliant with legal standards.
- Provides a verifiable record.
Cons:
- Slower process; may discourage users.
- Raises privacy and data storage concerns.
Best for: High-risk industries such as finance, gambling, or adult content.
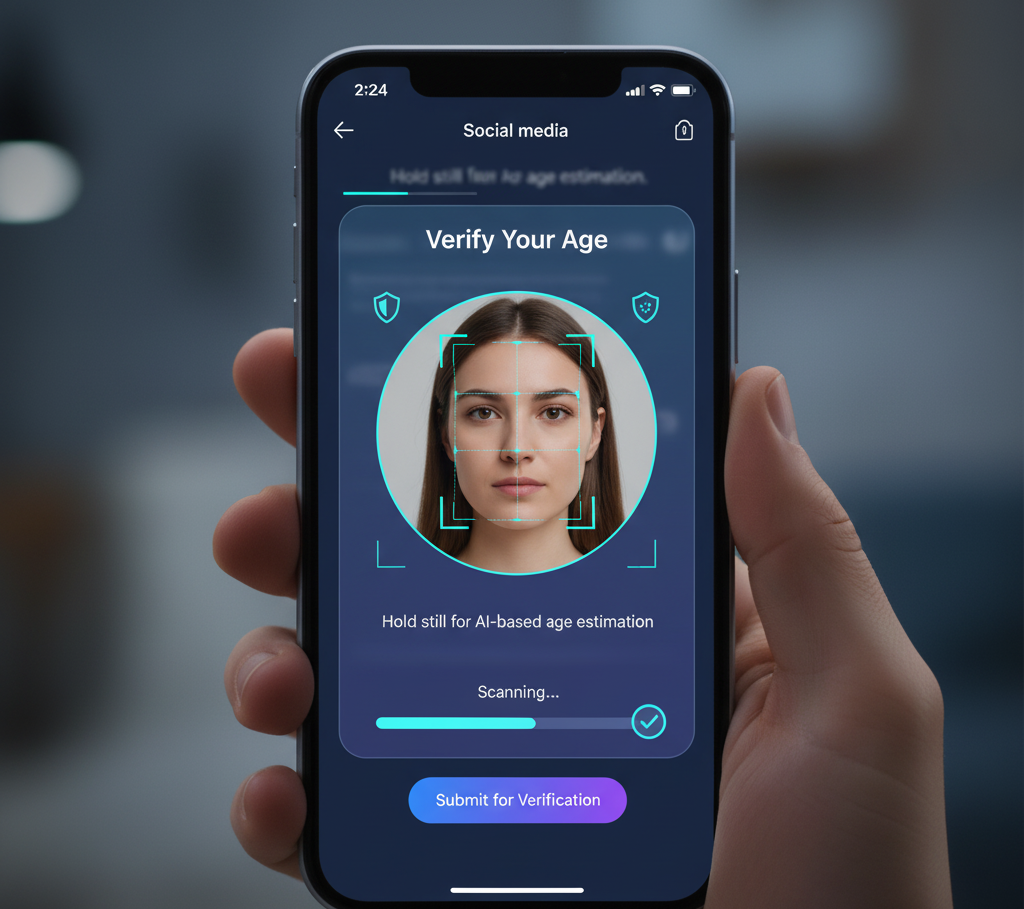
2. Biometric and AI-Based Methods
Modern systems use biometric data like facial scans or voice analysis to estimate age.
Examples:
- Facial recognition: Detects facial features and estimates age.
- Voice analysis: Identifies voice patterns related to age.
Pros:
- Quick and easy for users.
- No need to upload sensitive documents.
Cons:
- May show bias in certain demographics.
- Accuracy can vary with lighting, camera quality, and other factors.
Note: Many regulators are still debating how to handle biometric data securely.
3. Data Cross-Referencing
In this method, the system checks user information against existing databases like credit bureaus or public records.
Pros:
- Low friction for users.
- Scalable for large platforms.
Cons:
- May not work for younger users or those without public records.
- Raises data privacy issues.
4. Alternative Methods
Other verification options include:
- Credit card checks: Verifies adult ownership.
- Mobile network verification: Confirms age via carrier data.
- Parental consent: Parents verify and approve child access.
- Behavioral analytics: Uses browsing or interaction patterns to estimate age.
These methods are often used when document or biometric systems aren’t feasible.
5. Hybrid and Waterfall Approaches

Many platforms use multi-layered (hybrid) verification models — combining multiple methods for greater accuracy.
Example: A system might first use AI-based estimation, then request document verification if results are uncertain.
This “waterfall approach” balances speed, security, and user convenience effectively.
Current Challenges and Limitations
1. Privacy and Data Security Concerns
Collecting age data can expose users to privacy risks.
- Storing sensitive information like IDs or face data can lead to data breaches.
- Users fear surveillance or misuse of their personal data.
- Cross-border data transfer laws add further complexity.
Organizations must ensure strong encryption, anonymization, and consent management.
2. Technical and Accuracy Limitations
- False positives or negatives can occur, leading to wrongful access denials.
- AI systems may show bias across gender or ethnicity.
- Spoofing attempts (fake IDs, deepfakes) can trick systems.
- Performance may vary with device type or internet quality.
Continuous model training and independent audits help reduce these issues.
3. User Experience and Accessibility
Friction in sign-up processes can cause users to abandon registration.
Challenges include:
- Complex or slow verification steps.
- Lack of accessibility for disabled users.
- Poor support for low-bandwidth regions.
Balancing security with simplicity is crucial for long-term adoption.
4. Implementation and Cost Barriers
Implementing an advanced system isn’t easy:
- High setup costs for small platforms.
- Integration challenges with existing systems.
- Ongoing compliance updates required.
- Vendor management complexity.
However, cloud-based and API-driven solutions are making these systems more affordable.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
1. Social Media and Digital Platforms
Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube are under constant pressure to protect minors.
They now use AI-driven age checks, content filters, and parental tools to maintain compliance with laws such as the UK Online Safety Act.
2. Gaming and iGaming
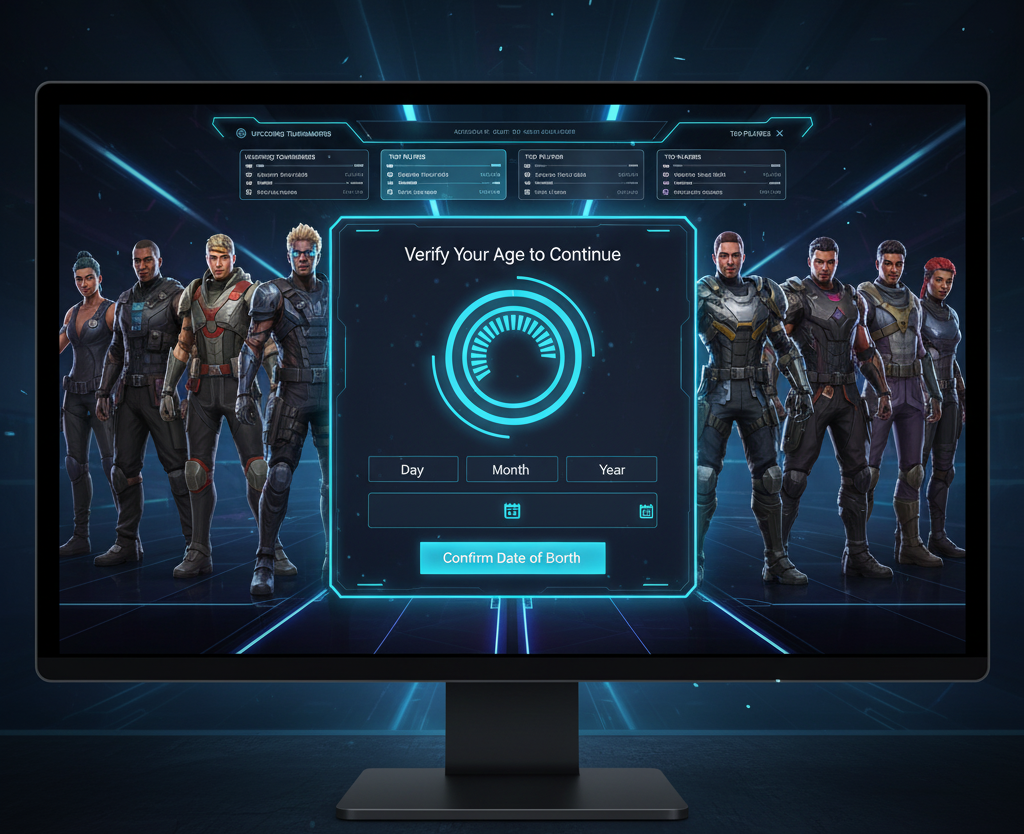
Age verification is vital in gaming to prevent underage gambling and fraud. Regulators require strict KYC (Know Your Customer) checks for online casinos and gaming platforms.
It also ensures responsible gaming and better player protection.
3. E-commerce and Retail
Online retailers must confirm age when selling restricted goods like alcohol or tobacco.
Vending machines and delivery services also use age verification APIs to confirm legal purchase age before transactions are completed.
4. Financial Services
Banks and fintech companies rely on age verification as part of KYC compliance.
It ensures users meet legal eligibility for account creation, loans, or investments.
5. Healthcare and Sensitive Services
In healthcare and telemedicine, age verification ensures only eligible patients can access certain consultations or medications.
Mental health apps also use it to provide age-appropriate services and resources.
Technology Trends and Innovations
Emerging Technologies
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP): Verify age without revealing personal data.
- Blockchain: Enables secure and tamper-proof identity verification.
- AI & Machine Learning: Improves accuracy of estimation systems.
- Decentralized Identity (DID): Gives users control over their own data.
These technologies make verification both secure and privacy-friendly.
Privacy-First Approaches
New privacy-preserving systems focus on:
- Data minimization (storing less data)
- On-device processing (no cloud uploads)
- Attribute-based verification (confirming only the needed info)
- Consent management for user transparency
These approaches help maintain user trust while staying compliant.
Industry Standardization Efforts
Several international organizations are working on global frameworks for age verification.
Goals include:
- Ensuring interoperability between systems.
- Defining data security best practices.
- Promoting ethical and inclusive verification models.
Best Practices and Implementation Guidelines
Choosing the Right Solution
- Assess platform risk level and legal needs.
- Evaluate vendors for accuracy, privacy, and scalability.
- Conduct a cost-benefit analysis before rollout.
- Plan for smooth integration with existing systems.
Privacy and Security Best Practices
- Encrypt sensitive data.
- Use secure servers and anonymization.
- Establish breach response protocols.
- Maintain clear consent forms for users.
User Experience Optimization
- Reduce friction with fast and simple verification steps.
- Communicate clearly why verification is required.
- Ensure accessibility for all users.
- Offer support channels for verification issues.
Compliance Management
- Regularly monitor changing laws.
- Keep audit trails and compliance reports.
- Manage cross-border regulations effectively.
- Continuously update systems for new standards.
Conclusion
Age verification has become a cornerstone of digital responsibility in 2025. It ensures compliance, protects minors, builds trust, and strengthens online ecosystems. The biggest challenge is to balance safety with privacy and convenience — but technology is rapidly improving this balance.




