Summary
In an increasingly digital world, verifying a person’s identity accurately and securely has become a top priority for organizations. Biometrics — the science of identifying individuals using unique biological traits — has emerged as one of the most powerful tools for authentication. However, as biometric systems become more common, fraudsters are finding new ways to manipulate them through spoofing and presentation attacks. To counter these challenges, modern biometric systems are incorporating vital sign detection and liveness detection to ensure that the biometric input truly comes from a living person, not a fake replica.
In this article, we’ll explore what biometrics (biometría) really means, how biometric authentication works, the importance of vital signs detection, and how these technologies work together to prevent identity fraud across industries.
Biometrics has revolutionized how we verify identity in our digital era. Whether it’s unlocking your smartphone with your fingerprint or using face recognition to verify your identity on a banking app — biometrics has become part of everyday life.
However, with every technological advancement comes a new wave of cyber threats. Fraudsters have developed sophisticated techniques such as presentation attacks and spoofing to trick biometric systems using fake fingerprints, videos, or even 3D masks.
To combat this, developers have integrated vital sign detection — a process that verifies the “liveness” of a biometric sample by analyzing indicators such as blinking, breathing, or pulse movement.
Before we explore how vital sign detection helps fight fraud, let’s first understand what biometrics truly means.
What is Biometrics: What Does “Biometría” Mean?

The term “biometría” comes from the Greek words bios (life) and metron (measure), meaning the measurement of life. In modern terms, biometrics refers to the measurement and analysis of people’s unique physical and behavioral traits to identify or authenticate them.
In simple words, biometrics answers the question: Are you really who you say you are?
Que es biometría (What is Biometrics)?
Biometría is the science of identifying individuals based on their unique biological characteristics. Unlike passwords (what you know) or ID cards (what you have), biometric authentication relies on what you are — your fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, or voice.
Que significa biometría (What does biometrics mean)?
Biometrics means using measurable human features to authenticate identity securely. It is considered one of the most reliable forms of authentication because biological traits are extremely difficult to replicate or steal.
Examen Biométrico (Biometric Examination)
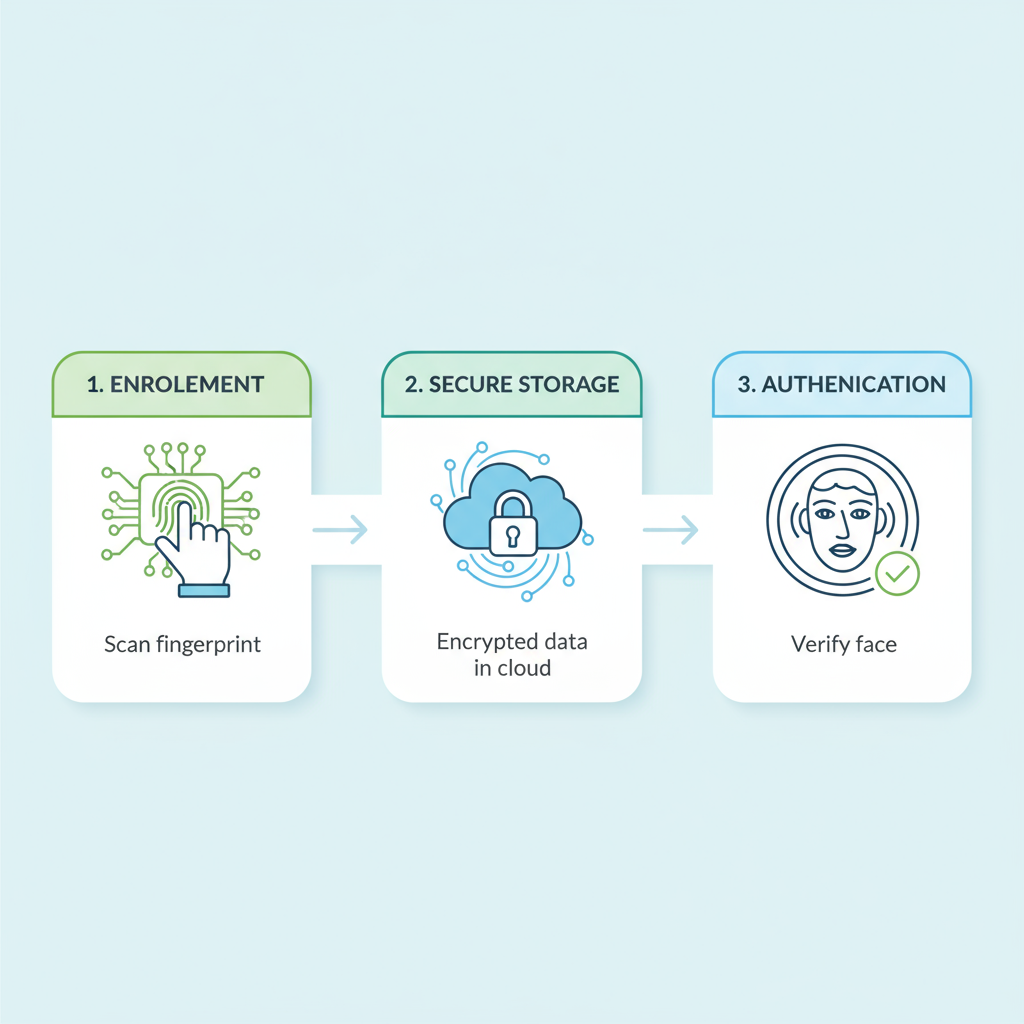
An examen biométrico or biometric examination refers to the process of collecting, analyzing, and verifying a person’s biometric data.
How It Works:
- Enrollment:
The person’s biometric trait (fingerprint, face, voice, etc.) is scanned and stored as a digital template. - Storage:
The system securely stores this data in encrypted form to protect privacy. - Verification/Authentication:
When the person returns, the system compares the live input with the stored data to confirm identity.
Biometric examinations are used in:
- Banking: eKYC, account opening, and secure transactions.
- Border Control: Passport verification and immigration checks.
- Healthcare: Patient identification and record protection.
- Corporate Security: Employee attendance and access control.
The Growing Threat: Presentation Attacks and Spoofing

While biometrics are more secure than passwords, they are not immune to fraudulent attacks.
A presentation attack happens when a fraudster presents a fake biometric sample — such as a photograph, video, or artificial fingerprint — to a sensor to trick the system.
Examples of Presentation Attacks:
- Using a printed photo or video clip to fool a facial recognition system.
- Creating a “gummy finger” made of silicone to bypass fingerprint scanners.
- Playing a recorded voice to deceive voice recognition systems.
- Using makeup, prosthetics, or altered physical features to hide one’s true identity.
These methods are dangerous because they can lead to identity theft, unauthorized access, and financial fraud.
To detect and prevent such attacks, biometric systems now include vital signs and liveness detection mechanisms.
What is a Presentation Attack?
A presentation attack is any deliberate attempt to deceive a biometric system. It aims to either:
- Impersonate another person (for example, using their facial image to log in), or
- Conceal one’s true identity (for example, using disguises to avoid recognition).
Types of Presentation Attacks:
- Impersonation Attack: The fraudster mimics someone else’s biometric traits.
- Spoofing Attack: The fraudster uses non-live representations like photos, masks, or recordings.
- Concealment Attack: The attacker modifies their own biometric traits to avoid detection.
Google’s biometric standards even classify these attacks as “imposter” and “spoofing” attacks, measuring detection strength using the security-strong acceptance rate (the percentage of undetected attacks), which should be 7% or lower for high-security systems.
What Is Vital Signs Screening and Liveness Detection?
Vital signs detection, often called liveness detection, refers to the process of confirming that the biometric sample belongs to a live human being and not an artificial replica.
Purpose:
To determine whether the source of a biometric input — such as a face or fingerprint — is live or fake.
Vital sign detection uses algorithms that analyze subtle physiological signals such as:
- Eye movements and blinking patterns.
- Breathing and pulse detection.
- Skin texture and micro-expressions.
- Voice intonation and lip movement synchronization.
This ensures that the person attempting authentication is physically present and alive.
Categories of Vital Signs Detection
There are two major types of vital signs detection methods: Active and Passive.
Active Vital Sign Detection
Active detection requires the user to perform a specific action during authentication.
Examples include:
- Asking the user to blink, turn their head, or smile.
- Speaking a randomly generated phrase for voice verification.
- Typing on a keyboard for keystroke rhythm analysis.
Advantages:
- Highly accurate.
- Very difficult for fraudsters to replicate.
- Can be combined with other modalities for multi-factor verification.
Passive Vital Sign Detection
Passive detection does not require any user interaction. Instead, it silently analyzes live data using advanced algorithms.
For example, a camera might detect subtle skin texture differences or micro-movements in breathing to confirm liveness.
Advantages:
- Completely seamless and user-friendly.
- Reduces friction during authentication.
- Ideal for mobile banking and e-commerce apps.
Many organizations use a combination of both active and passive detection to balance user convenience with security.
Facial Recognition and Vital Signs Detection
Facial recognition is one of the most popular biometric authentication methods, used widely in smartphones, airports, and online banking. However, it’s also one of the most targeted by spoofing attempts, mainly because facial images are easy to obtain through social media.
To prevent fraud, facial recognition systems now integrate vital signs detection technologies that analyze multiple indicators of liveness.
How Liveness Detection Works in Facial Recognition:
- Depth Sensing: Measures 3D facial structure to distinguish between real faces and flat photos.
- Texture Analysis: Detects reflections and irregularities that appear in fake materials like paper or masks.
- Motion Analysis: Identifies natural head movements, blinking, and breathing patterns.
- Multi-modal Verification: Combines facial recognition with voice or keystroke dynamics for enhanced accuracy.
By integrating these methods, systems can effectively detect spoofing attempts using videos, masks, or deepfake technology.
Role of Vital Signs Detection in Fraud Prevention
Vital signs detection plays a critical role in preventing fraud across multiple industries.
In Banking:
- Prevents fake account openings using false identities.
- Detects liveness during remote eKYC verification.
- Reduces phishing and account takeover risks.
In Telecommunications:
- Prevents SIM swap fraud and duplicate registrations.
- Ensures verified customers during customer service calls.
In Healthcare:
- Protects patient data and prevents identity misuse.
- Ensures that medical access is granted only to the verified individual.
In Border Security and Government ID Programs:
- Prevents duplicate identity registrations.
- Ensures authenticity of travelers during immigration checks.
In all these cases, vital sign detection acts as an invisible layer of defense that ensures every authentication event involves a real human being.
Metrics and Standards for Attack Detection
To evaluate biometric system reliability, several key performance metrics are used:
- APCER (Attack Presentation Classification Error Rate): Measures the rate at which spoofing attempts are incorrectly accepted as genuine.
- BPCER (Bona Fide Presentation Classification Error Rate): Measures how often genuine users are wrongly rejected.
- FAR (False Acceptance Rate): Probability of incorrectly verifying an imposter.
- FRR (False Rejection Rate): Probability of denying access to a legitimate user.
The goal is to minimize APCER and FAR while maintaining a balance between security and usability.
Google’s standard threshold for security-strong acceptance (7% or less) demonstrates how critical precision is in modern biometric systems.
The Future of Biometrics and Vital Sign Detection
The next generation of biometric systems will go beyond fingerprints and facial scans. The integration of AI, deep learning, and advanced sensors is making liveness detection even more sophisticated.
Emerging Trends:
- Thermal Imaging: Detects real human skin temperature to confirm liveness.
- Infrared and 3D Depth Sensors: Differentiate between real and fake objects.
- AI-Driven Behavioral Biometrics: Continuous monitoring of user behavior such as typing rhythm or navigation habits.
- Blockchain Integration: Decentralized storage of biometric data for enhanced privacy and tamper-proof authentication.
As technology evolves, biometric fraud detection will become faster, smarter, and more adaptive — capable of countering even deepfake-based identity theft.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its benefits, biometric technology also brings certain ethical and privacy challenges:
- Data Privacy: Biometric and vital sign data must be encrypted and handled with strict consent.
- Bias and Fairness: AI models must ensure accuracy across all genders, ethnicities, and age groups.
- User Awareness: People must be informed about how their biometric data is stored and used.
- System Dependence: Overreliance on biometrics can lead to lockouts if systems fail.
Addressing these challenges will be key to ensuring the ethical use of biometric systems in the years ahead.
Conclusion
Biometrics has transformed the way we authenticate identity, making security both stronger and simpler. However, as fraud tactics evolve, it’s vital to integrate vital signs detection and liveness verification to ensure that only real, live humans can access secure systems.
From preventing fake account openings in banks to stopping deepfake impersonations in mobile apps, biometrics combined with liveness detection is reshaping digital trust.
Ultimately, the future of biometric security lies in combining multiple modalities, AI-driven analytics, and continuous vital sign detection — ensuring that authentication remains fast, safe, and fraud-proof.
FAQs
Q1. Que es biometría?
Biometría es el uso de características físicas o de comportamiento únicas de una persona — como huellas dactilares, rostro o voz — para verificar su identidad.
Q2. Que significa biometría?
Significa la medición y el análisis de rasgos biológicos individuales para identificar o autenticar personas de forma segura.
Q3. What is a biometric examination (examen biométrico)?
It’s the process of capturing, analyzing, and matching biometric data to verify identity. Examples include fingerprint scans, facial recognition, and iris mapping.
Q4. What is a presentation attack?
A presentation attack is an attempt to fool a biometric system using fake representations like photos, videos, or masks.
Q5. How does vital sign detection prevent fraud?
It detects signs of liveness — such as blinking, breathing, or pulse movement — to ensure that the biometric data comes from a real, live person.
Q6. Is biometrics completely secure?
While highly secure, biometric systems must integrate liveness detection and comply with privacy regulations to ensure complete protection.
Debabrata Behera is a passionate blogger who writes about digital trends, personal growth, and practical insights, helping readers stay informed, inspired, and ready to achieve success in life.




