Timekeeping has come a long way since the Industrial Revolution’s first timeclocks, evolving to meet the needs of today’s dynamic and distributed workforce. Accurate tracking of employee time and attendance is crucial for businesses to ensure fair payroll, optimize productivity, and maintain compliance. Biometric time-and-attendance systems represent a modern, secure approach that eliminates common challenges such as fraud and errors inherent in traditional methods.
Understanding Biometric Time and Attendance
Biometric time and attendance systems use unique biological traits to verify an employee’s identity during clock-in and clock-out processes. Common biometric modalities include fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, voice authentication, and iris scanning. Unlike passwords or ID cards that can be shared or stolen, biometrics bind attendance data to a real individual, effectively preventing frauds like buddy punching and time theft.
How Biometric Time and Attendance Systems Work
The lifecycle of a biometric attendance system typically includes:
- Enrollment: An employee’s biometric data is captured and securely stored as a template on private servers. Duplicate records are prevented through one-to-many matching.
- Authentication: During each shift start or end, the employee’s live biometric sample is matched against stored templates.
- Liveness Detection: Advanced algorithms detect whether the biometric sample is live (e.g., a live face or fingerprint), protecting against spoofing attempts such as photos, videos, or masks.
- Mobile Capture & Location: Mobile apps enable remote or field workers to submit biometric attendance along with geolocation data to verify their presence at designated sites.
Advantages of Using Biometrics for Time and Attendance
- Increased Accuracy: Automated capture reduces human errors and eliminates falsified time entries.
- Enhanced Security: Identity verification via biometrics thwarts proxy punching and time theft.
- Convenience & Flexibility: Employees with flexible hours or remote locations can easily record attendance via mobile devices.
- Integration: Biometric systems can seamlessly connect with payroll and HR software, automating wage calculations and record keeping.
Also Check: What Is Age Verification And Why It Matters Today
Types of Biometric Systems for Workforce Management
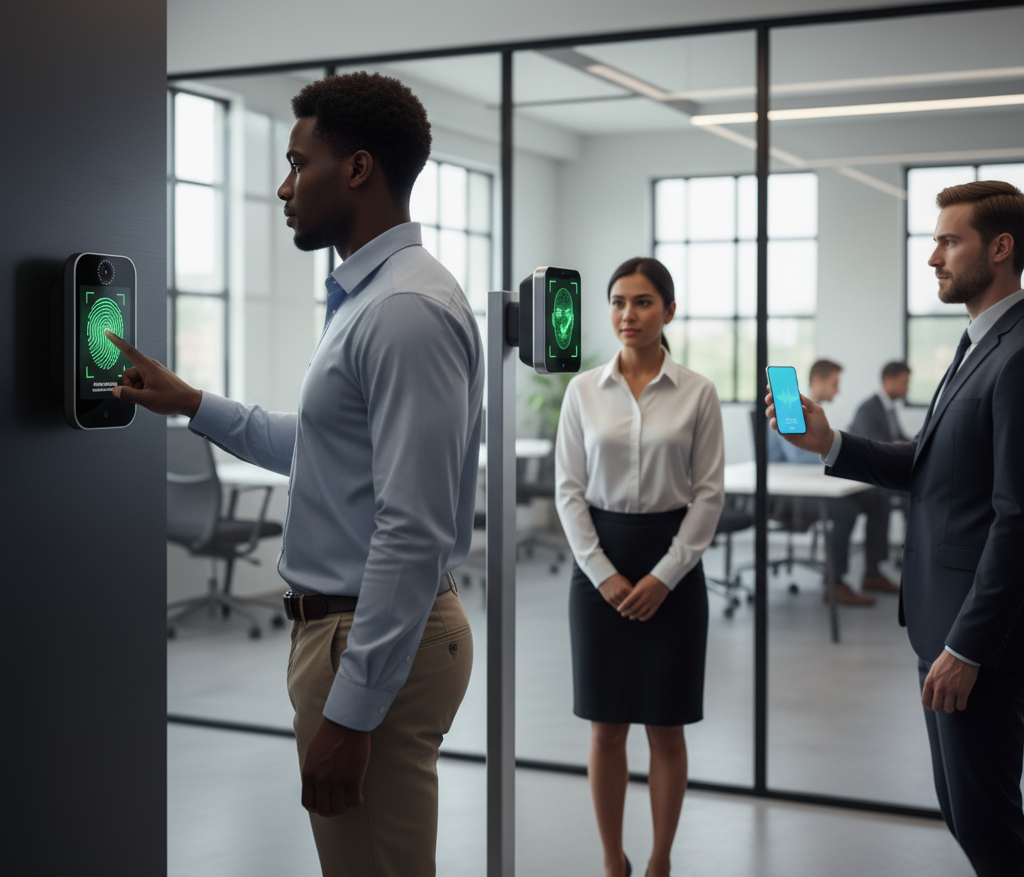

- Fingerprint Recognition: Cost-effective and widely used, ideal for fixed-location employees.
- Facial Recognition: Contactless and hygienic, suitable for offices and high-traffic environments.
- Voice Recognition: Enables hands-free authentication, beneficial in noisy or hands-busy settings.
- Iris Scanning: Offers the highest accuracy and security, used in critical or sensitive workplaces.
Addressing Privacy and Security Concerns
Biometric data is sensitive and must be protected under strict security protocols. Data templates are encrypted and stored on secure servers, ensuring no biometric information remains on individual devices. Compliance with privacy regulations involves transparent data handling policies, employee consent, auditing, and retention limits to protect personal privacy.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
- Manufacturing & Warehousing: Accurate shift tracking improves labor cost control and reduces overtime disputes.
- Corporate Offices: Speedy facial recognition systems reduce queues while enhancing building access control.
- Remote Workforce: Mobile biometric apps authenticate offsite employees with GPS-verified attendance logs.
Conclusion
Biometric time-and-attendance systems provide a reliable, fraud-resistant, and efficient framework for tracking workforce hours accurately across various industries and work environments. By integrating secure biometric technologies with HR and payroll systems, businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and foster trust through transparent attendance management.




